Phenology
Maine Wild Blueberry Phenology Guide
What is Phenology?
Blueberry phenology refers to the act of studying the steps of growing blueberries. These can also be called “growth stages”. This is important to be aware of when growing because it makes the steps very predictable and much simpler to plan. A big part of phenology is knowing (IPM) or integrating pest management. this includes: placement of beehives, fruit set monitoring, foliar nutrient sampling and knowing when to harvest.
All the information summarized on this page comes directly from the information in-depth phenology chart, and I would recommend taking a look at it for more details
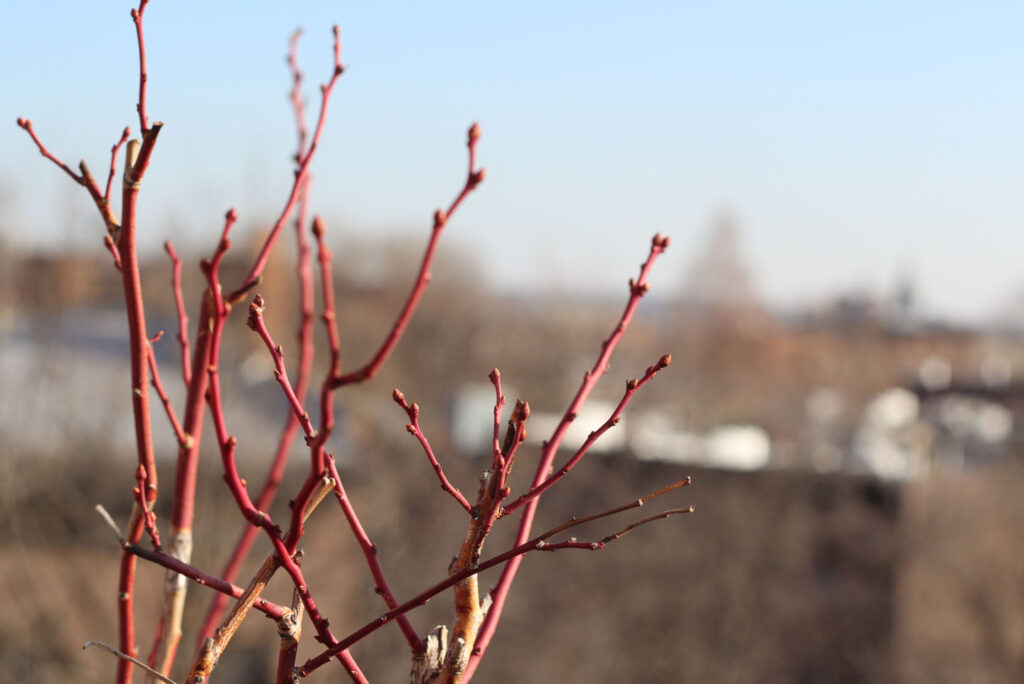
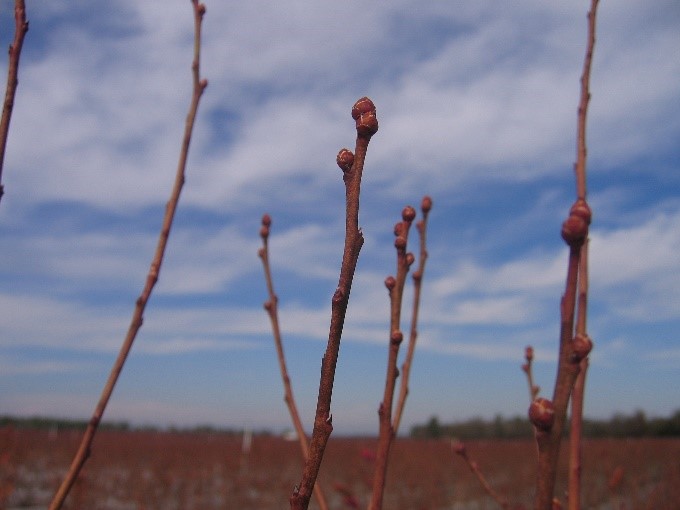
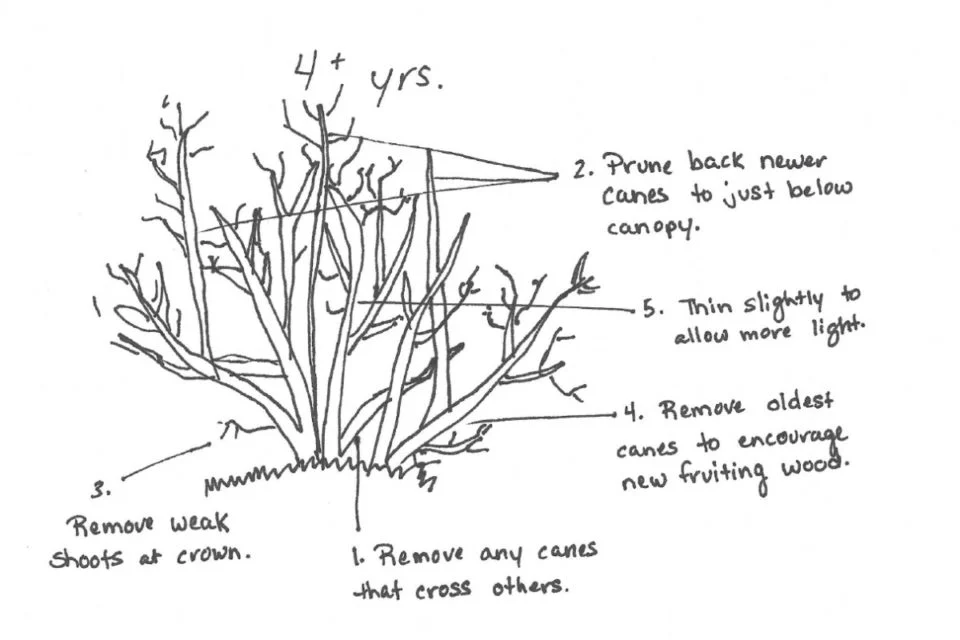
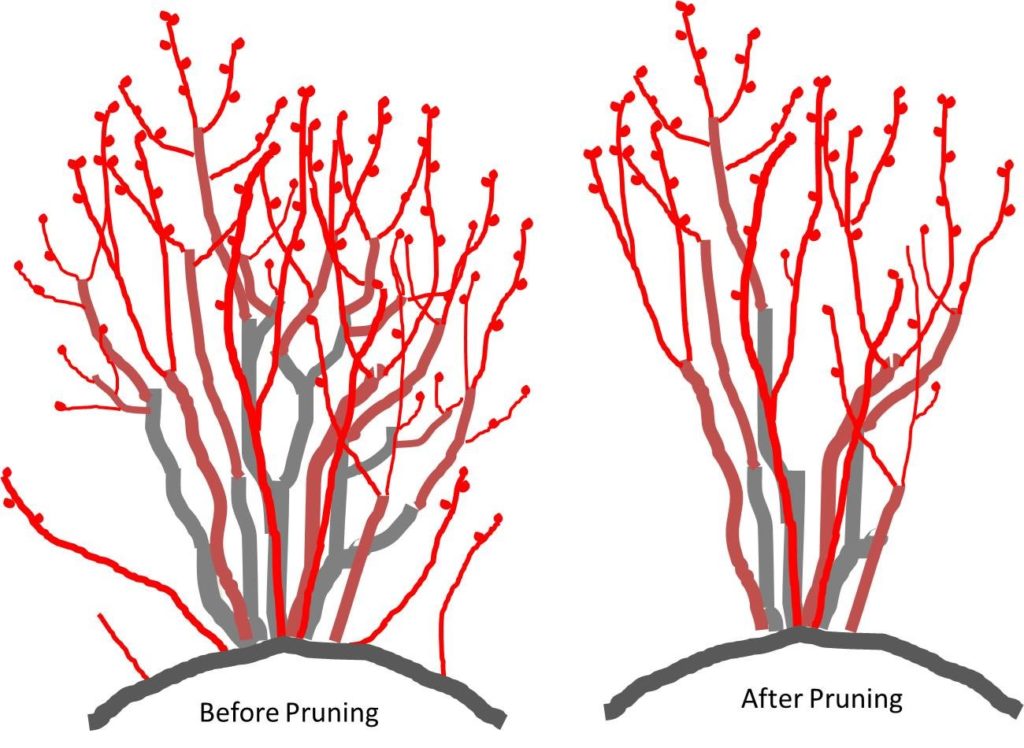


Prune Stage (Vegetative)
🍃 Leaf Emergence Stages (Vegetative):
Leaf emergence is the first step of cultivating blueberries and goes as follows
Early Green Tip 1/4: The very first signs of growth appear when green tips emerge from the buds. Extremely spikey green tissue emerges from the buds
Green Tip 2-3/4: As the green tissue continues to emerge from the buds, it start splitting up. This happens when they reach a certain range anywhere from 2-5mm. On the third step the spiked tips continue to separate above the 5mm mark.
Shoot Expansion 4/4: Finally, on the last part of the pruning or vegetative stage. The blueberry shoots grow larger, and the leaves begin to unfurl and create a ‘whorled’ pattern.
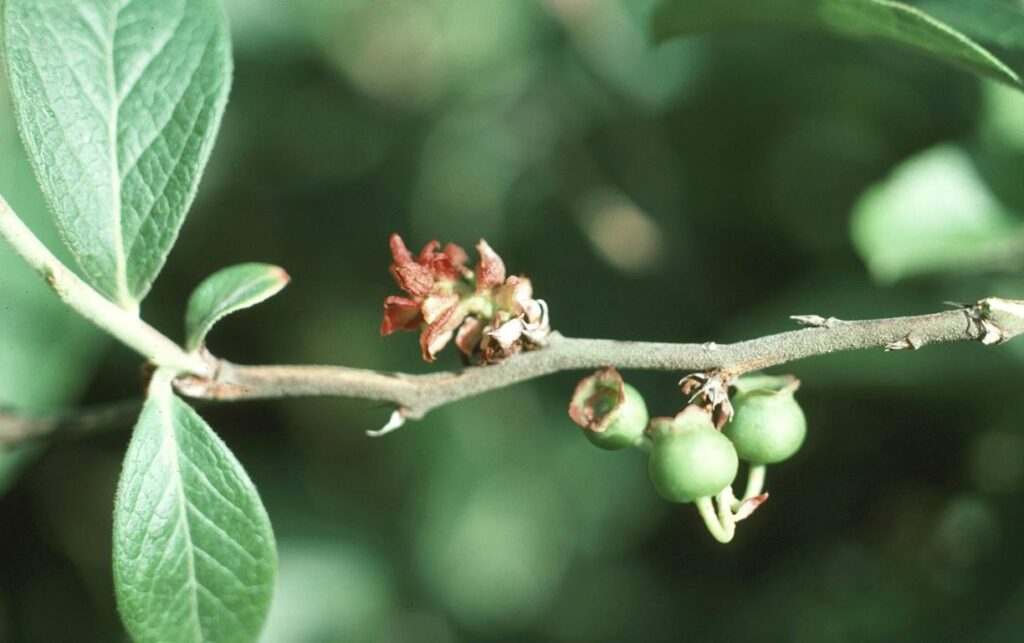
🍂 Tip Die Back (reproduction):
Tip Die Back: This is the stage where the plants transition from no longer having vegetative growth, but rather starting to reproductive growth. This process is called ‘budding,’ and it is a pivotal point in the life cycle of a blueberry bush as it shows if it will grow or not.
🌱 Bud Development:
This is the stage where the plant starts to mature and begin to grow blueberries
Bud initiation: The buds continue to swell as the starting point of the flowering process begins.
Scale development: The buds are becoming larger and rounder. They are taking on a reddish hue as they become more separate.
🍁 Leaf Drop & Bud Hardening:
- Leaf Drop: The wild blueberry is preparing for winter; it starts storing nutrients to preserve itself. The leaves start to turn red and will naturally fall off. Bud Hardening: The buds go from the original color of green, then to red, and then finally to a dark brown.
🌱 Crop Stage (Fruiting) – Wild Blueberry Phenology
🍃 Leaf Emergence Stages (Fruiting) :
Interestingly enough, the crop stage, despite being during the spring, shares the same steps as the pruning stage in early winter.
Early Green Tip 1/4: The very first signs of growth appear when green tips emerge from the buds. Extremely spikey green tissue emerges from the buds
Green Tip 2-3/4: As the green tissue continues to emerge from the buds, it start splitting up. This happens when they reach a certain range anywhere from 2-5mm. On the third step the spiked tips continue to separate above the 5mm mark.
Shoot Expansion 4/4: Finally, on the last part of the pruning or vegetative stage. The blueberry shoots grow larger, and the leaves begin to unfurl and create a ‘whorled’ pattern.
🌱 Bud Stages:
The first steps to bloom rather than for the leaves to fall off.
Bud Swell: The buds are starting to continue to ‘swell or get larger. At the same time, the flower inside the bud is becoming more noticeable and rounding out.
Early Bud Burst: As the buds are growing, they are becoming more distinct and separating a lot.
Bud Burst: Now the buds are completely separated from one another, making them their separate part of the plant. Now the flowers are rounding out more and starting to become more visible.
Tight Cluster: Finally, the leaves are fully visible and elongated; however, they are still tightly sealed in the bud.
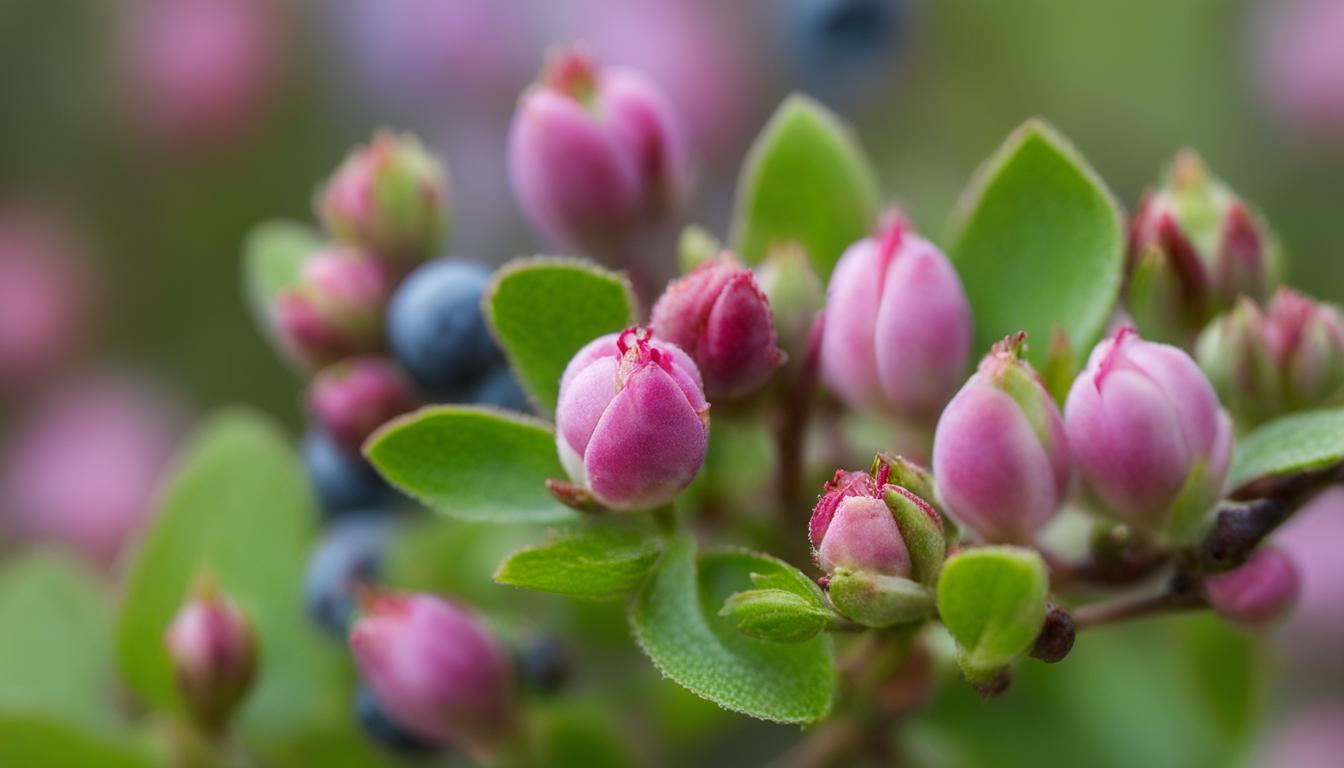
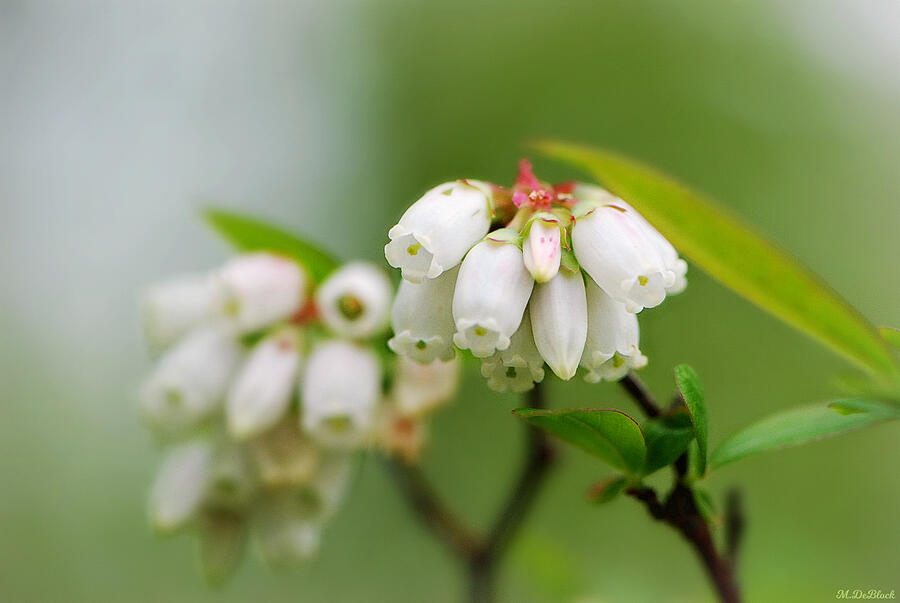
🌸 Bloom Stages:
Finally, it is here.
Early Flower: still within the bud, the pink leaves are now starting to emerge out of the green base, remaining closed.
Open Flowers: Finally, the flowers have bloomed. The buds have broken, showing a range from white to vivid pink petals. This is now the stage where pollination happens, and the plant can reproduce.
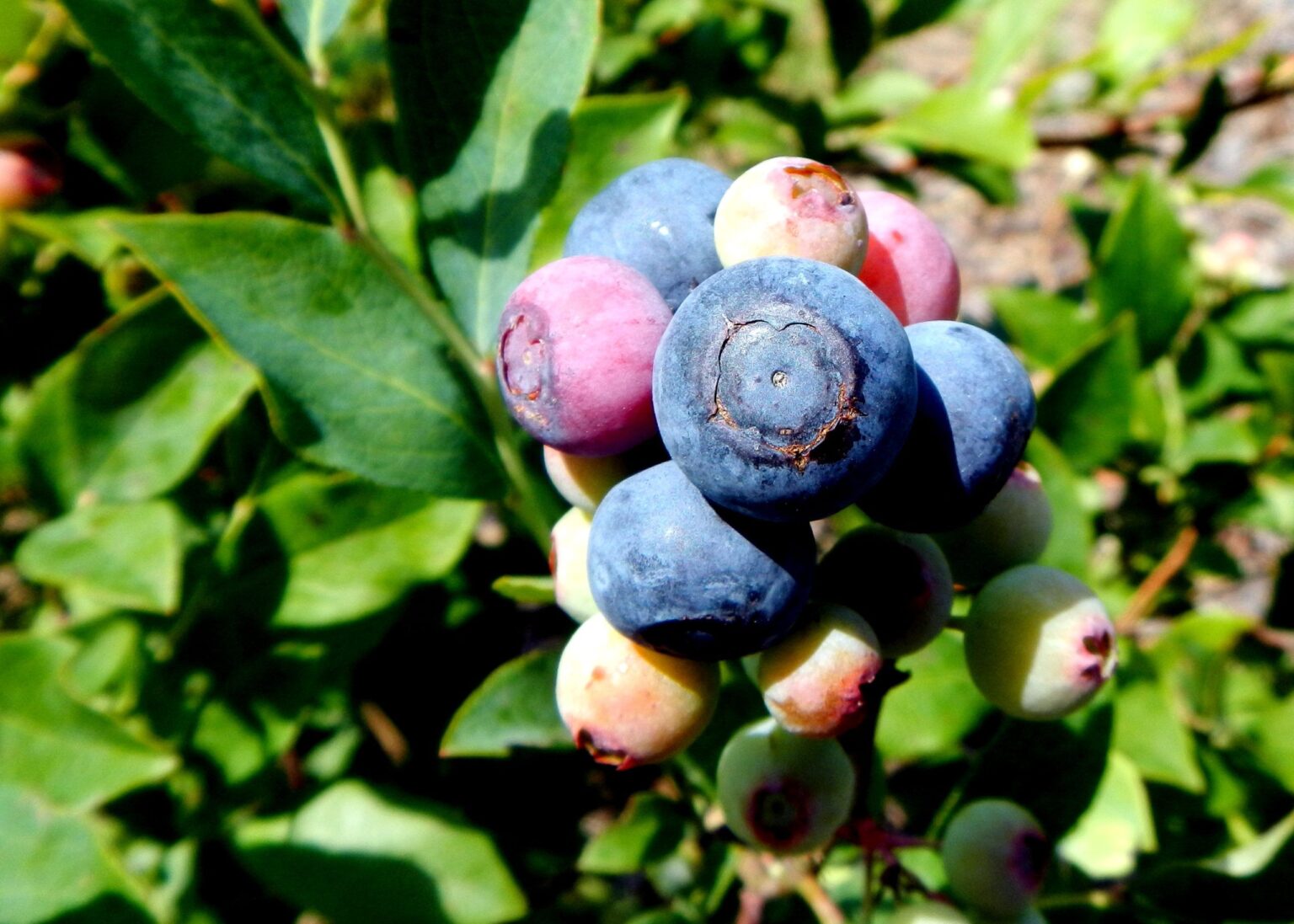
🫐 Fruit Development Stages:
From flowers to fruit
Petal Fall: After pollination, the flowers start to become weaker, often losing their colors, but this is a good thing! This means that the process has been accomplished, and the blueberries will start growing.
Early Green Fruit: The swell of fruit has begun; however, right now they are still hard and green and aren’t close to being grown.
Late Green Fruit: The ends of the fruit are starting to grow more. While still unripe, the color is starting to shift from the strong green to a more ambiguous color between green and red
Red Fruit: The previous green fruit is gone in its place are red fruit. While they are edible these are the blueberries you would find that are very sour due to the acid levels still being high.
Blue Fruit (Fully Ripened Berries): At last, the blueberries are fully ripened. They have a strong blue coloring and instead of a sour taste you get a sweet fruit that will keep you happy.






